Difference between revisions of "ADC max1027"
(→Hardware) |
(Intro refactoring) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | =Introduction= | |
| + | |||
| + | The MAX1027 is an 8 channels 10 bits analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with an internal reference and an internal temperature sensor. It is mounted (in option) on the [[APF9328]] boards.''' To know if you have one on your board, take a look at the connectors side:<br><br> | ||
[[Image:APF9328_with_MAX1027.jpg]] | [[Image:APF9328_with_MAX1027.jpg]] | ||
If you don't have one and are a good electronician, you can order a sample at [http://www.maxim-ic.com Maxim's website] and solder it directly on your board (footprint is available). | If you don't have one and are a good electronician, you can order a sample at [http://www.maxim-ic.com Maxim's website] and solder it directly on your board (footprint is available). | ||
| − | + | =Hardware interface= | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
'''The 8 inputs voltage range is [0 - 3,3V]. Don't try to put higher voltage on ADC inputs !!'''<br> | '''The 8 inputs voltage range is [0 - 3,3V]. Don't try to put higher voltage on ADC inputs !!'''<br> | ||
By default internal reference voltage is used ('''2,5V'''), so if you apply analog values > 2,5V, they will be truncated.<br> | By default internal reference voltage is used ('''2,5V'''), so if you apply analog values > 2,5V, they will be truncated.<br> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 14: | ||
If you want to use the MAX1027 then you will have to connect #EOC pin (End Of Conversion) to an i.MXL GPIO, configured as Interrupt (see apf9328.c for more details). By default the driver is using CSI_D6 (PortA 10) pin. | If you want to use the MAX1027 then you will have to connect #EOC pin (End Of Conversion) to an i.MXL GPIO, configured as Interrupt (see apf9328.c for more details). By default the driver is using CSI_D6 (PortA 10) pin. | ||
| − | + | =Driver= | |
For the Linux kernel, the Max1027 is considered as a [http://lxr.linux.no/source/Documentation/hwmon/sysfs-interface?v=2.6.18 Hardware Monitoring] device. | For the Linux kernel, the Max1027 is considered as a [http://lxr.linux.no/source/Documentation/hwmon/sysfs-interface?v=2.6.18 Hardware Monitoring] device. | ||
For the moment only a low speed interface (/sys) is available: the eight channels and the temperature are updated every 10ms. | For the moment only a low speed interface (/sys) is available: the eight channels and the temperature are updated every 10ms. | ||
| Line 89: | Line 87: | ||
# let conv=0x84; echo $conv > /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/conversion | # let conv=0x84; echo $conv > /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/conversion | ||
| − | + | =Links= | |
* [http://datasheets.maxim-ic.com/en/ds/MAX1027-MAX1031.pdf MAX1027 datasheet on Maxim website] | * [http://datasheets.maxim-ic.com/en/ds/MAX1027-MAX1031.pdf MAX1027 datasheet on Maxim website] | ||
* [http://lxr.linux.no/linux+v2.6.23.1/Documentation/hwmon/sysfs-interface hwmon documentation] | * [http://lxr.linux.no/linux+v2.6.23.1/Documentation/hwmon/sysfs-interface hwmon documentation] | ||
Revision as of 10:56, 12 September 2008
Contents
Introduction
The MAX1027 is an 8 channels 10 bits analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with an internal reference and an internal temperature sensor. It is mounted (in option) on the APF9328 boards. To know if you have one on your board, take a look at the connectors side:
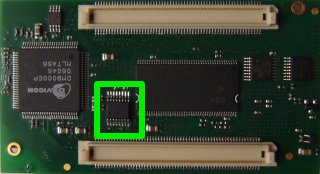
If you don't have one and are a good electronician, you can order a sample at Maxim's website and solder it directly on your board (footprint is available).
Hardware interface
The 8 inputs voltage range is [0 - 3,3V]. Don't try to put higher voltage on ADC inputs !!
By default internal reference voltage is used (2,5V), so if you apply analog values > 2,5V, they will be truncated.
The i.MXL SPI_1 interface is used to communicate with the device.

If you want to use the MAX1027 then you will have to connect #EOC pin (End Of Conversion) to an i.MXL GPIO, configured as Interrupt (see apf9328.c for more details). By default the driver is using CSI_D6 (PortA 10) pin.
Driver
For the Linux kernel, the Max1027 is considered as a Hardware Monitoring device. For the moment only a low speed interface (/sys) is available: the eight channels and the temperature are updated every 10ms.
Installation
- From the top directory:
$ make linux-menuconfig
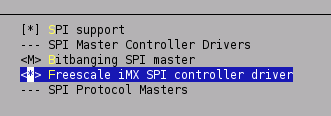
- Then select in Device Drivers->SPI support->Freescale iMX SPI controler driver (builtin not module !!)
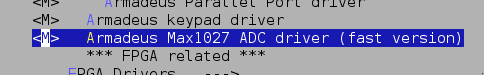
- Then select in Device Drivers->Hardware Monitoring Support->MAX1027 sensor chip (Module)
- Once the new config saved, rebuild your image
$ make
and copy hwmon.ko and max1027.ko driver to your target or reflash your rootfs.
- On the target, the driver can be started like this:
# insmod /lib/modules/drivers/hwmon/hwmon.ko # insmod /lib/modules/drivers/hwmon/max1027.ko
- or like this if you reflashed your rootfs:
# modprobe max1027
Usage
"Slow" interface (for temperature or battery level measurements)
Several interfaces in /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi... are created in order to:
- read the 8 analog inputs values: inx_input (in mV)
- read the temperature: temp1_input (in m°C)
- modify the max1027 registers: conversion, setup & averaging
An input can be read like that:
# cat /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/in0_input
The temperature can be read like that:
# cat /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/temp1_input
These values are only updated each time you launch a conversion and are only dedicated to measure slow evolving greats.
"Fast" interface (frequencies > 10Hz)
In that case you can use /dev interface (using blocking read to wait end of conversion). To create /dev nodes you can use the loadmax.sh script. As driver MAJOR number is dynamically allocated, you may need to update /dev depending on the drivers loaded on you system.
- repeatedly read value of analog input 0 (variable sampling rate = depends on system load):
# cat /dev/max1027/AIN0
- read analog input 0 once:
# time dd if=/dev/max1027/AIN0 bs=2 count=1 > tmp.bin # hexdump tmp.bin
Chip registers configuration
Independent of the mode, /sys interfaces allow direct access to the corresponding register in the MAX1027:
# let conv=0xb9; echo $conv > /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/conversion
You can also get current (hexadecimal) values of conversion, averaging and setup registers with (for example):
# cat /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/setup 0x62
For more details on how to use these registers, take a look at the datasheet.
Shell examples
- Get channel 0 and temperature values:
# let conv=0x87; echo $conv > /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/conversion # cat /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon0/device/temp1_input # cat /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon0/device/in0_input
- Get channels [0-7] and temperature values:
# let conv=0xb9; echo $conv > /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/conversion
- Get 4 average values (of 32 conversions) for channel 0:
# let avg=0x3c; echo $avg > /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/averaging # let conv=0x84; echo $conv > /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/conversion
Links
| Other languages: | |
|---|---|
|
| |