Difference between revisions of "Communicate"
m (→Server configuration) |
m (→Server configuration) |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | A more detailed [[Target_Software_Installation#Configure_U-Boot|U-Boot configuration is in Setup Basics here]] | |
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
Revision as of 23:48, 2 March 2009
How-To connect your Armadeus board to your development Host.
Contents
Forewords
The default connection uses a simple RS232 Null-Modem cable (with or without USB<->serial adapter).
As you will have to transfer some mega bytes of data, the Ethernet link is mandatory.
In order to use these two media with the APF target a terminal emulator (for RS232 link) and a TFTP server (for Ethernet link) have to be configured.
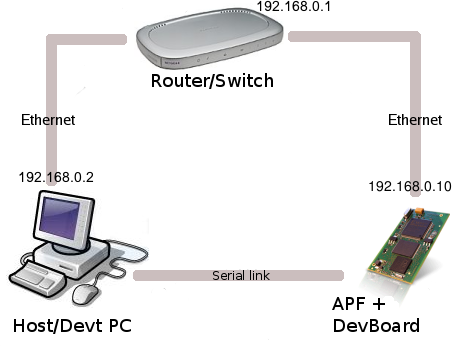
At this stage, you should have something looking like that (IP addresses may change):
RS232 Terminal configuration
You will need a RS232 terminal emulator to communicate with U-Boot/Linux console. You can choose between:
- Kermit
- Minicom
- GtkTerm
We suggest you to use Kermit as Terminal emulator for RS232 connection. Minicom was sadly reported to have problems when communicating with U-Boot (ZModem data transfer). If you just need a simple serial console and not to transfer data through RS232, then GTKTerm is the perfect choice ! (package gtkterm in Ubuntu)
TFTP server
In order to send your image files (U-Boot, Linux, rootfs or FPGA's firmware) at higher speed to your Armadeus board, you can use the Ethernet link and a TFTP server. Once the server started, the files located in the server shared directory (/tftpboot by default) will be accessible from the U-Boot/Linux TFTP clients.
TFTP server installation
- On *Ubuntu / Debian:
[ ] $ sudo apt-get install tftpd xinetd
or use Synaptic
- On Fedora:
[ ] $ rpm -q tftpd xinetd
- Then create the directory that will contain all the files that the server will export (you have to be root to do that):
[ ] $ sudo mkdir /tftpboot [ ] $ sudo chmod 777 /tftpboot
Server configuration
- Edit or create the configuration file /etc/xinetd.d/tftp and modify/add it the following lines:
# default: off
# description: The tftp server serves files using the trivial file transfer
# protocol. The tftp protocol is often used to boot diskless
# workstations, download configuration files to network-aware printers,
# and to start the installation process for some operating systems.
service tftp
{
socket_type = dgram
protocol = udp
wait = yes
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd
server_args = -s /tftpboot
# disable = yes
}
- Restart xinetd service:
[ ] $ sudo killall -HUP xinetd
- Put some files in /tftpboot
- To test it from U-Boot:
BIOS> setenv serverip 192.168.0.2 (the IP address of your tftp server/PC hosting the files to download)
BIOS> tftp ${fileaddr} apf9328-linux.bin
MAC: 00:1e:ac:00:00:01
operating at 100M full duplex mode
TFTP from server 192.168.0.2; our IP address is 192.168.0.10
Filename 'apf9328-linux.bin'.
Load address: 0x8000000
Loading: #################################################################
######################################################
done
Bytes transferred = 1604984 (187d78 hex)
BIOS>
A more detailed U-Boot configuration is in Setup Basics here