OneWire GPIO bus Master
From ArmadeusWiki
Informations and HOWTOs for Armadeus OneWire support.
Author: User:JanosA
Contents
Supported boards and software versions
- Use the latest Armadeus GIT/SF repository or the latest stable release.
- Currently, with APF28 modules, only the APF28Dev board is supported, but it's easy to add support to another boards. (Check linux-2.6.35.3/arch/arm/mach-mx28/apf28dev.c file)
- Following instructions were also successfully tested on OPOS6ULDev.
Software installation
- If not done bye default, recompile your Linux kernel with OneWire GPIO bus master (and some slave device) support.
$ make linux-menuconfig
Device Drivers --->
<*> Dallas's 1-wire support --->
1-wire Bus Masters --->
<*> GPIO 1-wire busmaster
1-wire Slaves --->
<*> Thermal family implementation
$ make
- Reflash your Linux kernel
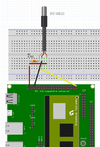
Hardware Notes
| APF28Dev | OPOS6ULDev |
|---|---|
* Vcc 3.3V is pin 1 on J9 connector * DQ is pin 31 on J9 (LCD_D18 / GPIO 1_18) * GND is pin 39 on J9
|
|
How it works
The OneWire bus master driver every 10 seconds scan the bus for new slave devices.
Each detected OneWire slave device have a sub-directory with it's unique ID in "/sys/devices/w1 bus master".
The sub-directory format is <2 digit family ID>-<12 digit unique ID>.
# ls -la /sys/devices/w1\ bus\ master/ total 0 drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 0 Jan 1 01:06 . drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 0 Jan 1 01:05 .. drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 0 Jan 1 01:06 28-000001e68904 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 01:07 driver -> ../../bus/w1/drivers/w1_master_driver drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 Jan 1 01:07 power lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 01:07 subsystem -> ../../bus/w1 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 uevent -rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_add -r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_attempts -r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_max_slave_count -r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_name -r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_pointer -rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_pullup -rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_remove -rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_search -r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_slave_count -r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_slaves -r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 01:07 w1_master_timeout
You can list the detected slaves from this files:
# cat /sys/devices/w1\ bus\ master/w1_master_slave_count 1 # cat /sys/devices/w1\ bus\ master/w1_master_slaves 28-000001e68904
Let's read the temperature: (The 28-xxx family is a DS18B20 temperature sensor in this example.)
# cat /sys/devices/w1\ bus\ master/28-000001e68904/w1_slave dd 01 4b 46 7f ff 03 10 1e : crc=1e YES dd 01 4b 46 7f ff 03 10 1e t=29812
The t=29812 means, the temperature is: 29.812°C