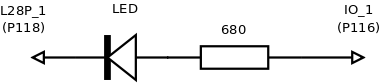
Simple blinking LED
This design introduce FPGA usage on APF. The design will allow you to synthesize a design and configure the FGPA to blink a LED.
| |
Note:
For APF9328_devlight you will have to connect a LED as described on figure 1. On all others DevBoard, a led is already soldered on FPGA |
Contents
[hide]The design
The VHDL code above describe a clock divider by 48000000 to generate a 0.5 Hz clock that will blink the LED.
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
use IEEE.numeric_std.all;
entity Clk_div_led is
Port (
Clk : in std_logic;
led_cathode : out std_logic;
led_anode : out std_logic
);
end Clk_div_led;
architecture RTL of Clk_div_led is
constant max_count : natural := 48000000;
signal Rst_n : std_logic;
begin
Rst_n <= '1';
led_cathode <= '0';
-- 0 to max_count counter
compteur : process(Clk, Rst_n)
variable count : natural range 0 to max_count;
begin
if Rst_n = '0' then
count := 0;
led_anode <= '1';
elsif rising_edge(Clk) then
if count < max_count/2 then
led_anode <='1';
count := count + 1;
elsif count < max_count then
led_anode <='0';
count := count + 1;
else
count := 0;
led_anode <='1';
end if;
end if;
end process compteur;
end RTL;
To synthesize this code, use Xilinx Web Pack, create a new project and add this VHDL module.
ISE need to know where to branch LED pins on its IO, this pinout is describe in constraint file with extension .ucf.
- For APF9328:
# Clock at 96MHz
NET "Clk" LOC = "P55";
NET "Clk" TNM_NET = "Clk";
TIMESPEC "TS_Clk" = PERIOD "Clk" 10 ns HIGH 50 %;
# LED
NET "led_cathode" LOC = "P118"| IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 ;
NET "led_anode" LOC = "P116"| IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 ;
- For APF27
# Clock at 100MHz
NET "Clk" LOC = "N9"; # CLK0
NET "Clk" TNM_NET = "Clk";
TIMESPEC "TS_Clk" = PERIOD "Clk" 10 ns HIGH 50 %;
# LED
NET "led_cathode" LOC = "C15"| IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 ; #IO_L24N_1
NET "led_anode" LOC = "C16"| IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 ; #IO_L24P_1
- For APF51
TODO
Some constraint files example can be found in Armadeus BSP's firmware/ directory.
Generate bitstream
Once these two files are written, FPGA configuration file, also named "bitstream", can be generated by clicking on Synthetize - XST then Implement Design and finally Generate Programming File. If all these operations are correctly done, a file with ".bit" extension will be generated.
Configure FPGA
To configure FGPA the bitstream must be downloaded from Host to APF's memory and then from APF's memory to FPGA.
Host to APF
Downloading Bitstream from Host to APF can be done in different way : with tftp from U-Boot, with tftp from Linux, with serial from U-Boot or with nfs from Linux. Here the file is downloaded with tftp in U-Boot:
- First copy bitstream in the host tftp directory:
cp blinking_led_apfXX_200k.bit /tftpboot
- Then download it in APF ram with U-Boot command :
BIOS> tftpboot ${loadaddr} blinking_led_apfXX_200k.bit
dm9000 i/o: 0x15c00000, id: 0x90000a46
MAC: 00:0e:32:00:00:01
operating at 10M half duplex mode
TFTP from server 192.168.0.143; our IP address is 192.168.0.10
Filename 'Clk_div_led.bit'.
Load address: 0x8000000
Loading: T ##########################
done
Bytes transferred = 131029 (1ffd5 hex)
APF to FPGA
Finally, to download bitstream in FPGA (to configure the FGPA) use the U-Boot fpga command:
BIOS>fpga load 0 ${loadaddr} ${firmware_len}
FPGA configuration can also be done in Linux.
Enjoy the beauty of a blinking LED
To see the LED blinking, the FPGA bank must be powered as explain in the datasheet.