ADC max1027
Contents
Introduction
The MAX1027 is an 8 channels 10 bits analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with an internal reference and an internal temperature sensor.
Only 7 channels can be used (AIN0-AIN6) when AIN7 is configured as "start of conversion".
As the MAX1027 is a quite complicated component to drive (because of its versatility), we recommand to read its datasheet before going further.
Driver
Depending on your needs (ie sampling slow or fast signals) there are 2 ways to use the max1027 Linux driver:
- for slow signals (temperature or battery level monitoring), the driver can be strictly controlled from its /sys interface: /sys/bus/spi/devices/spiN.0/ (N depending on the number of SPI devices declared for your target). Moreover, if needed (lm-sensors & Co), you can add it a Linux Hardware Monitoring API (hwmon) compatible/standardized interface: /sys/class/hwmon/hwmonN/device/ (N depending on the ID given by hwmon). This interface mimics the /sys/bus/spi/devices/ one.
- for "fast" signals, the driver has a /dev interface which can be configured through /sys/bus/spi/devices/spiX.0/.
Installation
Max1027 driver is now by default installed on standard rootfs. so these instructions are kept here as reference.
Usage
- On the target, the driver can be started like this:
# modprobe max1027 max1027 v0.5 successfully probed !
"Slow" & configuration interface
Several interfaces in /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi... are created in order to:
- read the 7 analog inputs values: inx_input (in mV)
- read the temperature: temp1_input (in m°C)
- modify the max1027 registers: conversion, setup & averaging
# ls /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/ averaging driver in2_input in5_input modalias temp1_input bus in0_input in3_input in6_input setup uevent conversion in1_input in4_input in7_input subsystem
An input can be read like that:
# cat /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/in0_input
The temperature can be read like that:
# cat /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/temp1_input
"Fast" interface (frequencies > 10Hz)
In that case you can use the /dev interface (using blocking read to wait end of conversion). To create /dev nodes you can use the loadmax.sh script located in armadeus/target/linux/modules/max1027 (driver's MAJOR number is dynamically allocated, so /dev needs to be dynamically created).
# loadmax.sh
- if not already installed:
$ cp target/linux/modules/max1027/loadmax.sh /tftpboot/
# tftp -g -r loadmax.sh 192.168.0.X (192.168.0.X = your Host PC's IP address) # sh loadmax.sh
- first, the conversion mode has to be chosen (channel 0->6 and temp):
# let set=0xb1; echo $set > /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/conversion
- and eventually the averaging and setup registers as well (refer to the max1027 documentation for more details):
# let set=0x48; echo $set > /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/setup # let set=0x20; echo $set > /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/averaging
- then you can for example repeatedly read value of analog input 0 (variable sampling rate = depends on system load):
# cat /dev/max1027/AIN0 | hexdump
- read analog input 0 once:
# time dd if=/dev/max1027/AIN0 bs=2 count=1 > tmp.bin # hexdump tmp.bin
This mode is activated by default in the Max1027 driver. If you switched to "slow" mode you can activate "fast" mode again with:
# let set=0x48; echo $set > /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/setup
Chip registers configuration
Independent of the mode, /sys interfaces allow direct access to the corresponding register in the MAX1027:
# let conv=0xb1; echo $conv > /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/conversion
You can also get current (hexadecimal) values of conversion, averaging and setup registers with (for example):
# cat /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/setup 0x62
For more details on how to use these registers, take a look at the datasheet.
Shell examples
- Get channel 0 and temperature values:
# let conv=0x87; echo $conv > /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/conversion # cat /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon0/device/temp1_input # cat /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon0/device/in0_input
- Get channels [0-6] and temperature values:
# let conv=0xb1; echo $conv > /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/conversion
- Get 4 average values (of 32 conversions) for channel 0:
# let avg=0x3c; echo $avg > /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/averaging # let conv=0x84; echo $conv > /sys/bus/spi/devices/$ADC_SPI/conversion
MAX1027 on APF27Dev board
The MAX1027 is optionnaly mounted on the APF27Dev board. It is ready to use and the ADC inputs can be accessed through J6
MAX1027 on APF9328 board
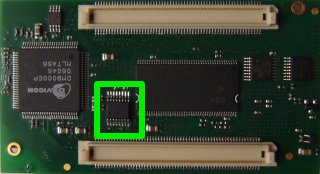
It is mounted (in option) on the APF9328 boards. To know if you have one on your board, take a look at the connectors side:
If you don't have one and are a good electrician, you can order a sample at Maxim's website and solder it directly on your board (footprint is available).
Hardware interface
By default internal reference voltage is used (2,5V), so if you apply analog values > 2,5V, they will be truncated. The i.MXL SPI_1 interface is used to communicate with the device.
On APF9328
By default the driver is using:
- PA13 (CSI_HSYNC) for #EOC
- and PA14 (CSI_PIXCLK) for #CNVST
So for example on the APF9328DevFull board you will have to connect:
- pin 11 of ADC connector (right of the Ethernet one) to pin 12 of CSI connector (below RS232 one)
- and pin 10 of the ADC connector to pin 9 of the CSI connector
On APF27Dev
Nothing special to do: MAX1027 is already set in "fast mode" and using #EOC and #CNVST pins.
Links
| Other languages: | |
|---|---|
|
| |