Communicate
How-To connect your Armadeus board to your development Host.
Contents
Forewords
The default connection uses a simple RS232 Null-Modem cable (with or without USB<->serial adapter).
As you will have to transfer some mega bytes of data, the Ethernet link is mandatory.
In order to use these two media with the APF target a terminal emulator (for RS232 link) and a TFTP server (for Ethernet link) have to be configured.
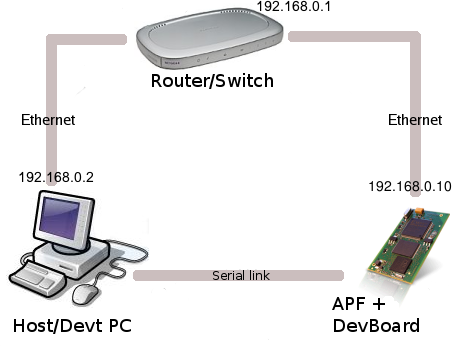
At this stage, you should have something looking like that (IP addresses may change):
Serial Terminal configuration
You will need a Serial terminal emulator to communicate with U-Boot/Linux console. You can choose between:
We suggest you to use Kermit as Terminal emulator. Minicom was sadly reported to have problems when communicating with U-Boot (ZModem data transfer). If you just need a simple serial console and not to transfer data through the serial link, then GTKTerm is the perfect choice ! (gtkterm package in Ubuntu)
TFTP server
In order to send your image files (U-Boot, Linux, rootfs or FPGA's firmware) at higher speed (than serial port) to your Armadeus board, you can use the Ethernet link and a TFTP server. Once the server configured, the files located in the server shared directory (/tftpboot by default) will be accessible from the U-Boot/Linux TFTP clients.
TFTP server installation
- On *Ubuntu / Debian:
[ ] $ sudo apt-get install tftpd xinetd
or use your preferred graphical package manager
- On Fedora:
[ ] $ rpm -q tftpd xinetd
- Then create the directory (/tftpboot/) that will contain all the files that the server will export:
[ ] $ sudo mkdir /tftpboot [ ] $ sudo chmod 777 /tftpboot
Server configuration
- Edit (as root user) or create the configuration file /etc/xinetd.d/tftp and modify/add it the following lines:
# default: off
# description: The tftp server serves files using the trivial file transfer
# protocol. The tftp protocol is often used to boot diskless
# workstations, download configuration files to network-aware printers,
# and to start the installation process for some operating systems.
service tftp
{
socket_type = dgram
protocol = udp
wait = yes
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd
server_args = -s /tftpboot
# disable = yes
}
- Restart xinetd service:
[ ] $ sudo killall -HUP xinetd
For more information regarding how-to setup a tftp server please check one of many web how-to:
- TFTP server quick how-to
- Another how-to configure a TFTP Server for Linux
- till another how-to...
- ubuntu TFTP server documentation in French
Errata
It looks like xinetd configuration is not sufficient in new versions. IPv6 is enabled by default and seems to be not compatible with the TFTP protocol. A simple inetd configuration should work for people who have this problem (connection refused in logs with addresses like ::ffff:192.168.0.100).
- Edit (as root user) - if necessary - the /etc/inetd.conf file and add this line:
tftp dgram udp wait nobody /usr/sbin/tcpd /usr/sbin/in.tftpd -s /tftpboot
- Install inetd tools
On Ubuntu/Debian
armadeus# sudo apt-get install inetutils-tools
- Setup the hosts rules: edit (ass root user) /etc/hosts.allow and add the following lines:
in.tftpd: ALL tftpd: ALL
- Restart inetd
armadeus# sudo /etc/init.d/openbsd-inet restart
It's done... and should work for most people.